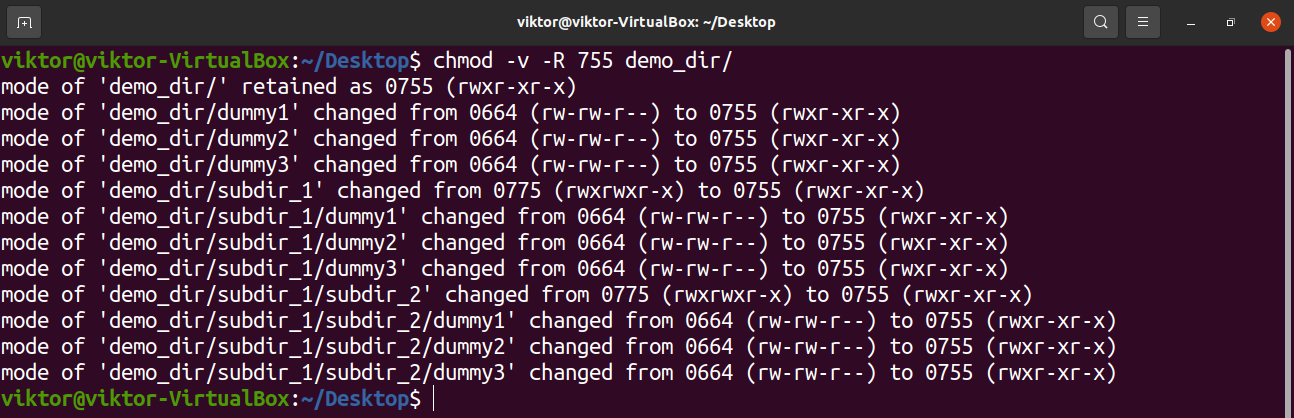
chmod 755 /exampledirectory/ In many cases, the permissions should also be changed recursively on all files and subdirectories This can be done through chmod by using the R option To change all permissions for files within a directory to read and write for the owner, read for the group, and read for other users, run the following command For example $ chmod 755 R directory_name $ chmod 755 R /home/linuxtechi/data Example 3) Assign permissions using text notation Another way of assigning permissions is by using the text notation In this method, the chmod command takes flags or symbols which represent the owner, group, others or all users ( u, g , and o) in the syntaxThe chmod command when given a number basically treats it as a 4 digit octal number, octal ( base 8) as in the digits 0 to 7 , where the position from left to right are special ;

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do By Claudio Sabato Medium
Chmod 755 example
Chmod 755 example- For example If one file has mode 740 rwxr , setting mode u=rwX,g=rX,o=rX with ansible, you will get 755 rwxrxrx instead the expected 644 rwrr Despite that this is not what you wanted, it will make the file executableThe number defined after chmod represents the permissions The chmod 775 is an essential command that assigns read, write, and execute permission to a specific user, group, or others In this guide, check out how to use chmod 755 Chmod basics Before diving deeper, let's have a look at the basics of chmod



Chown
In addition to these beautiful answers I want to mention a small but probably important difference The command chmod 755 file is equivalent to chmod 0755 file If we run this command on a file which has the SETUIDbit or SETGIDbit set, it will remove the SETUID/SETGIDbit chmod x file will leave the SETUID/SETGIDbit untouched We can seeThe group permission is 5 and others permission is 4 Therefore, the commands that use numbers to represent permissions arechmod 754 file For example, there's one in my directoryfile2File, current permissions arerwrr(644), now change torwxrxrx(755), execute the command $ chmod 755 file2You can Description of other parameters chmod Examples Permissions Using Numeric mode Setting Read/Write/execute to owner Read/execute to group and everyone else to example1txt chmod 755 example1txt #rxwrxrx Copy Setting Read/Write to owner Read/execute to group and read only to everyone else to example2txt chmod 664 example2txt #rwrwr– Copy
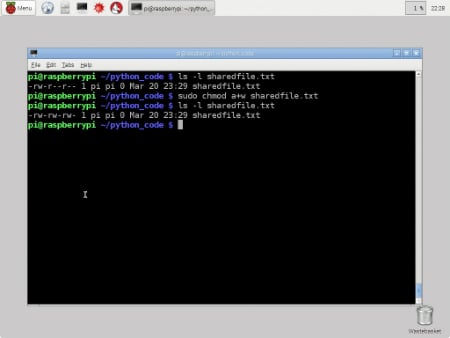
For example, umask 000 means anyone has read, write, and execute permissions on all newly created files Let's say we want to set more restrictive permissions for the newly created files and directories so others will not be able to cd to the directories and read files What is the difference between umask and chmod? A 777 permission on the directory means that everyone has access to read/write/execute (execute on a directory means that you can do a ls of the directory) 755 means read and execute access for everyone and also write access for the owner of the file When you perform chmod 755 filename command you allow everyone to read and execute the file, owner To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod R assigns to both Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples To change permission of only files under a specified directory
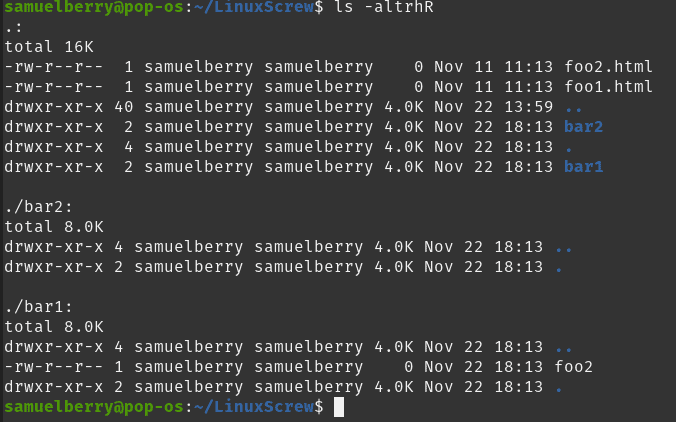
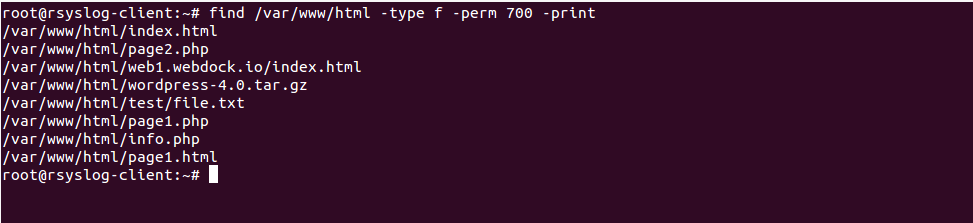
For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www directory to 755 you would use $ chmod R 755 /var/www Operating on Symbolic Links Symbolic links always have 777 permissions By default, when changing symlink's permissions, chmod will change the permissions on the file the link is pointing toTo assign 755 permission of all files and directories under /opt/dir # chmod c R 755 /opt/dir This would also remove any special permission if already assigned to any of the files or directories under /opt/dir For example, I created a file with Sticky Bit Special permission under /opt/dir You can use find if you can define some wildcard For example find name "*sh" exec chmod 755 {} ;




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize




Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
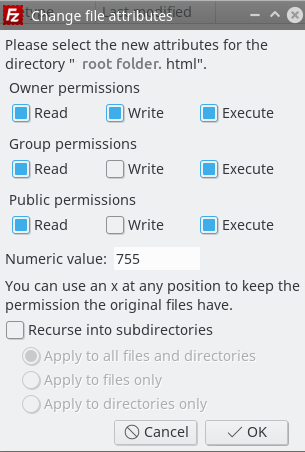
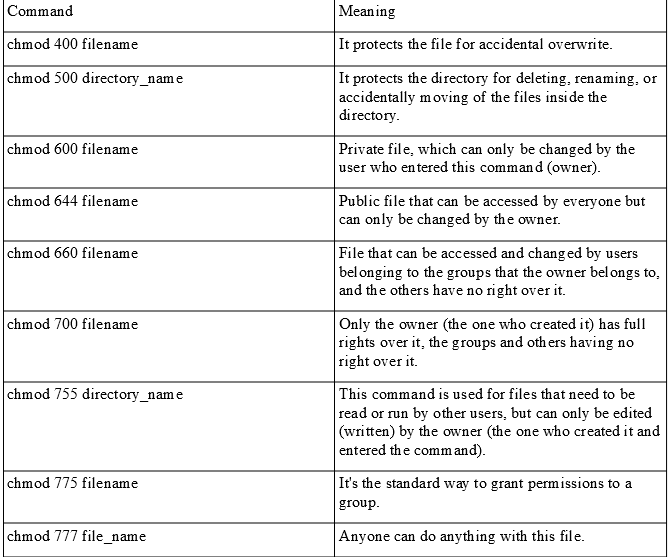
In the first command, for the 'others' clearly I haven't given any ownership to the files and in the second command I am giving read and execute permission to others (chmod 755) So what will exactly happen now?Chmod mode = 0755 Numeric Mode Examples Allow read permission to everyone $ chmod 444 file Allow everyone to read, and execute the file $ chmod 755 file Make a file readable by anyone and writable by the owner only $ chmod 644 file Make a file readable and writable by the group and others $ chmod 066 file Symbolic ModeView (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 755 (chmod arwx,gw,ow) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily
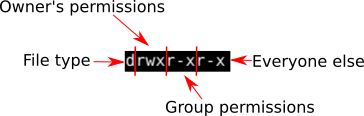



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples



How To Change Store S Root Folder Permissions Chmod 755 Cart2cart Faq
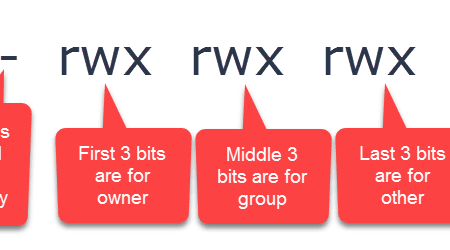
Examples To Change group ownership In our case I am using group1 as a group in the system To change ownership we will use chown group1 file1txt You can see that the group permissions changed to group1 from root, if you use v option it will report that We just need to add a "" to change group Chmod 755 means that the owner has full read, write, and execute privileges while the group has read and execute permissions, and the other group has read and execute permissions Let me use an analogy, person A (Owner) is the owner of the file so he has full permission do what ever he wants with the file read, write, execute (7)Specifies the new permissions The mode parameter consists of four numbers The first number is always zero The second number specifies permissions for the owner The third number specifies permissions for the owner's user group The fourth number specifies permissions for everybody else Possible values (to set multiple permissions, add up



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do By Claudio Sabato Medium
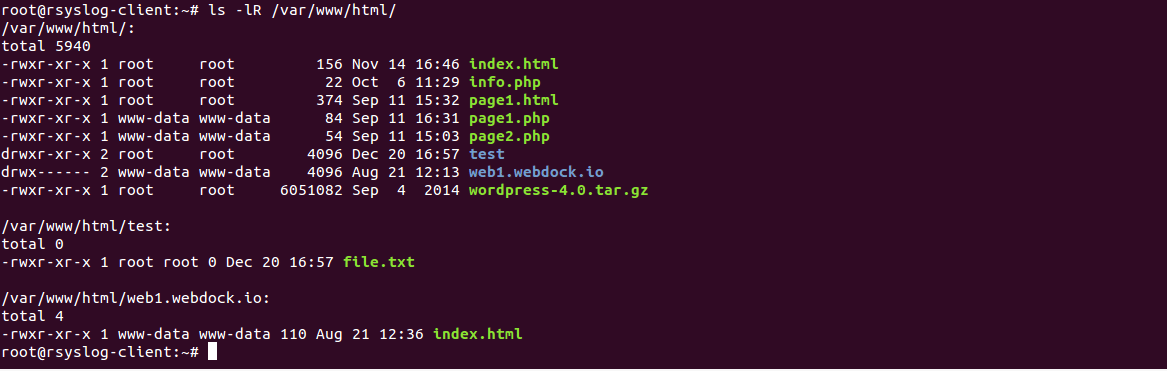
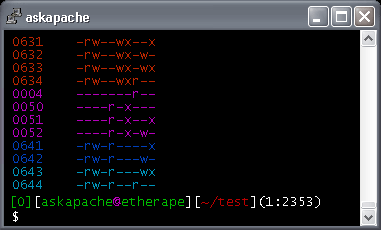
chmod examples using octal mode First column shows the chmod command , second column shows how the value is calculated for the permission last columns of owner, group, others shows individual octal values and actual bit set on file as seen by ls l For setting any other permission combination for owner, group & other , pick correspondingEveryone Else In this case there are 3 digits given For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www/html directory to 755 you would use chmod R 755 /var/www/html The mode can also be specified using the symbolic method




Recommended File Permissions For Wordpress Asdqwe Dev




Javarevisited 10 Examples Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
Chmod gowx mydir This denies group members and others the permission to create or delete files in mydir (gow) and allows group members and others to search mydir or use it in a path name (gox) This is equivalent to the command sequence chmod gw mydir chmod ow mydir chmod gx mydir chmod ox mydirTo put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users rwrr 1 john john 272 Mar 17 02 testtxt In the above example User (john) has read and write permission Type chmod 755 * to change mode for all files in that directory If you only want to change mode for a special type of file your can use chmod 755 *txt *dat orchmod 755 filenameext FTP In this example we're going to use WS FTP, but you can use any other FTP software that support chmod UNIX




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather



Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively
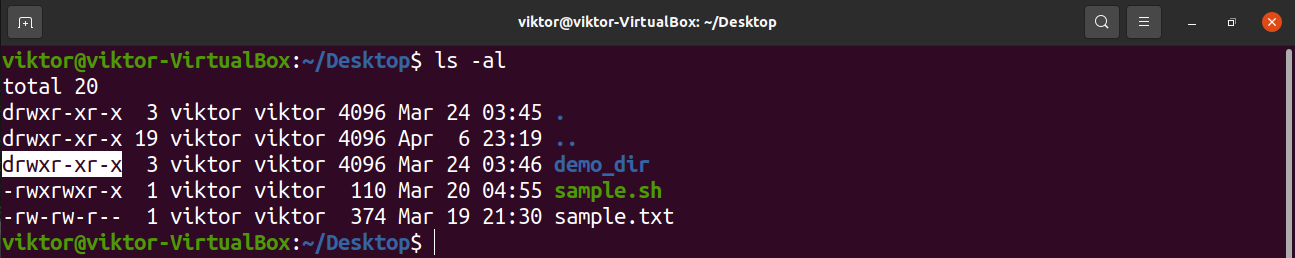
A 777 permission on the directory means that everyone has access to read/write/execute (execute on a directory means that you can do an ls of the directory) 755 means read and execute access for everyone and also write access for the owner of the fileWhen you perform chmod 755 filename command you allow everyone to read and execute the file, the For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www directory to 755 you would use chmod R 755 /var/www Operating on Symbolic Links # Symbolic links always have 777 permissions By default, when changing symlink's permissions, chmod will change the permissions on the file the link is pointing to chmod 755 symlink Now, let us see how chmod command can be used to change the access mode of a file Example 1 Let's change the assgn1_clientc permission so that the owner cannot write (w) in the file but can only read it BEFORE rwrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc COMMAND chmod u=r assgn1_clientc AFTER rrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc Before




Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples



Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies
In the following example, assume that pathname was assigned a value earlier in the exec This example changes the mode of the file to readwriteexecute for the owner, and readexecute for all others "chmod (pathname) 755" Parent topic Syscall command descriptions chmod 755 tutorial , chmod 775 , chmod recursive chmod permissions ssh permissions in Linux Unix , operation not permitted Example to Understand Chmod 775 If you enter a command ls la or ls li or ls l , any of these commands will show all the files like this drwxrxrx 2 amiss amiss 4096 TemplatesChmod 775 Chmod 775 (chmod arwx,ow) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute (G)roup can read, can write and can execute (O)thers can read, can't write and can execute



Hello Gui Help How Do I Give It Permission To Run Chmod 755 Update Hash Sh Tutorials Examples Holochain Forum



Hello Gui Help How Do I Give It Permission To Run Chmod 755 Update Hash Sh Tutorials Examples Holochain Forum
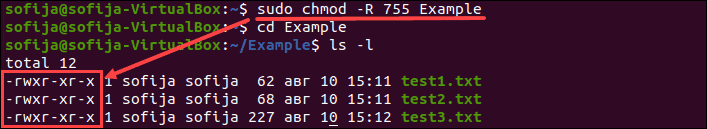
$ chmod 764 somefiletxt The numeric system is often used by applications and web hosting services because it is more concise than the letters Take a look at this common example $ chmod 755 somethingphp In many cases, you'd only want the owner to write the file, but web servers to be able to read and execute it Closing Thoughts sudo chmod R 755 Example The command gives read, write, and execute privileges to the owner (7) and read and execute access to everyone else (55) Note In the example above, the permission is defined using the octal/numerical mode (755) chmod is Linux command used to change file permissionschmod changes user, group and other read, write and execute permissionchmod 755 is popular use case for chmod chmod 755 is generally used to make most of the operations without problem because it provides ease for system administrators while running applications chmod 755 755 can be separated as




Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Note In the example above, the permission is defined using the octal/numerical mode (755) Alternatively, you can utilize the symbolic mode (using alphanumerical characters) and use the command chmod R u=rwx,go=rx Example Change Permission With the find Command To assign separate permissions to directories and files, you can use the findHdfs dfs chmod 755 /hadoop/file1 Changes permissions of the file hdfs dfs chmod R 755 /hadoop Changes permissions of the files recursively hdfs dfs chown ubuntuubuntu /hadoop Changes owner of the file 1st ubuntu in the command is owner and 2nd one is group hdfs dfs chown R ubuntuubuntu /hadoop Changes owner of the files recursivelyChmod commandIn this article, I'll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command I'll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod rBefore you see the chmod examples, I would strongly advise you to learn the basics of file permissions in Linux Using chmod command will be a lot easier once you




How To Set File Permissions On Mac How To




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




The Chmod Command



Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It



Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples




Command Line What Is The Difference Between Chmod X And Chmod 755 Ask Ubuntu



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux




Agenda The Linux File System Chapter 4 In Text Setting Access Permissions Directory Vs File Permissions Chmod Utility Symbolic Method Absolute Method Ppt Download



Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com



What Is The Chmod 777 Filename Sh Used For Quora




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Change Linux S Permissions Through A Practical Example Of The Chmod Command




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode




What Does 755 Permissions Mean In Unix



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf




Csci 243 C Unix Kirk Anne South 124a Ppt Download




Linux Commands Chmod




Linux Chmod Command Dracula Servers Tutorials




Difference Between Locate Which And Find Command In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Change Folder Permissions Command Line Terminal Mac X



1




Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin



Chown



Unable To Chmod 755 For A File That Should Be Created On An External Volume Issue Moby Moby Github




Understanding File Permissions




Chmod 755 775 Recursive Ssh Permissions Chmod 775 Vs 777



Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Chmod 644 755 777 What S The Difference Linuxpip




Linux Chmod Command Examples Journaldev




Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions



1




Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube




Why Not To Use Chmod 777 Pi My Life Up



Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Linux Permissions Making Sense Of 755 And Rwxr Xr X Serverwise




Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org



How To Use Chmod




Chmod Recursively Change Files And Folders Permissions Recursively In Linux Linuxtect




Chmod 755



Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux




ベストコレクション Chmod 777 Command In Linux With Examples 無料の車の画像



Chmod All Files To 644 All Folders To 755 Of A Directory Nixpal



Understanding Linux File Permissions 755 And Rwxr Xr X Datamounts
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



Chmod




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech



Changing Permissions On A File In Linux Mvps Net Blog




What Is Ftp Chmod Chmod Change Mode Impress Org



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples




Chmod Wikipedia




Ftp Rights 755 Vs 777 Newbedev




Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks




How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize




8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut




How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu
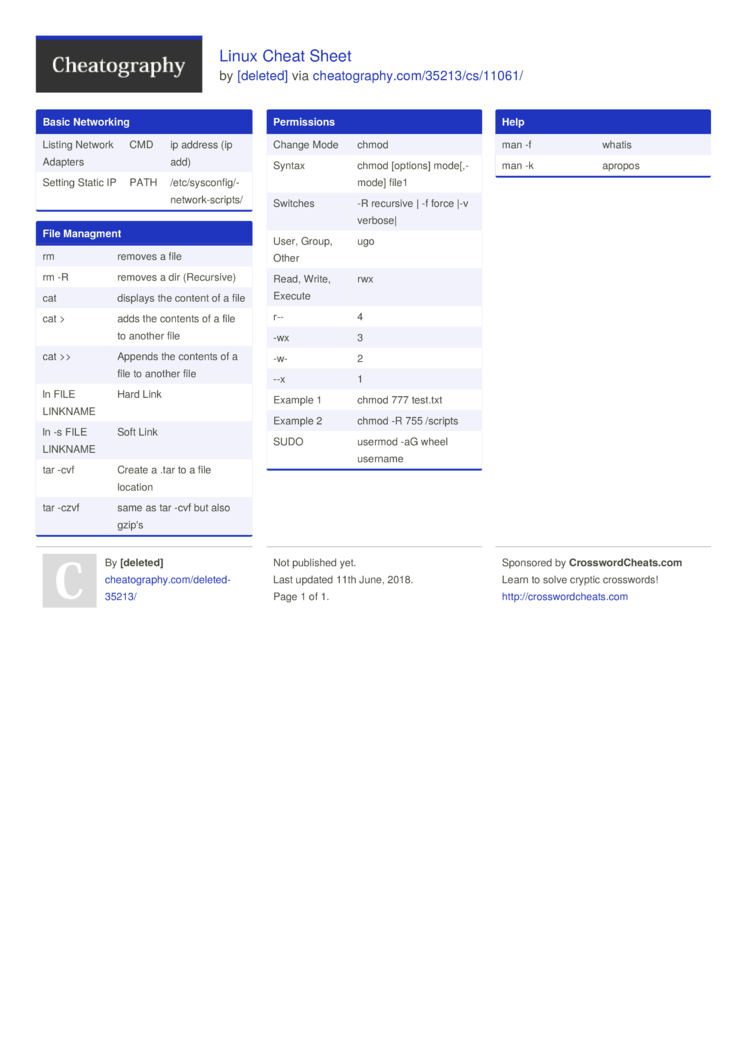



Linux Cheat Sheet By Deleted Download Free From Cheatography Cheatography Com Cheat Sheets For Every Occasion




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier
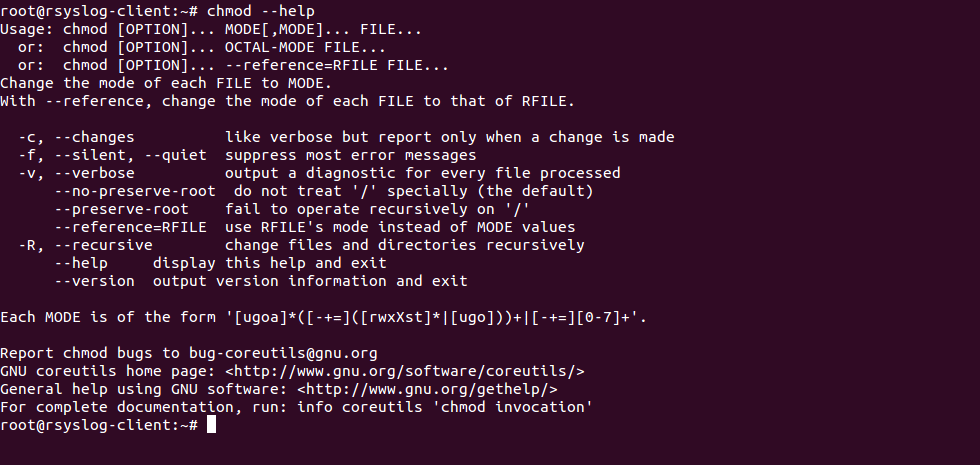



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders



Change Permissions For Files And Folders In Linux Utilize Windows




August 21 21 What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It Holhol24




Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base




Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize




A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler
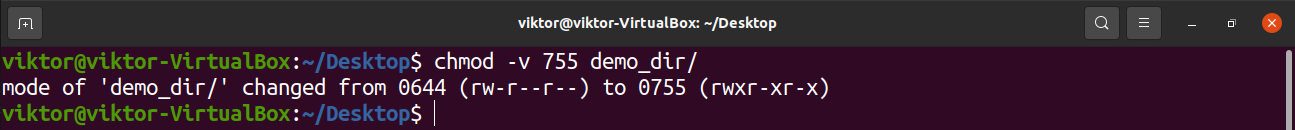



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
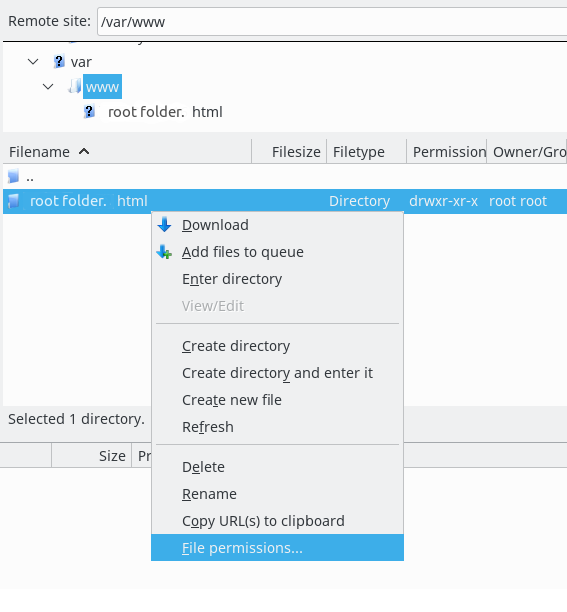



How To Change Store S Root Folder Permissions Chmod 755 Cart2cart Faq



How To Set File Folder Permissions To 755 Or 644 In Windows Quora




This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux




Chmod Not Working Software Web Applications Lawrence Systems Forums




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




Introduction To Linux Unix You Can Have Many




How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux The Wise Bulb



Introduction To Vi Bash Scripts And Ftp




What Does Chmod 755 Do Quora



Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿